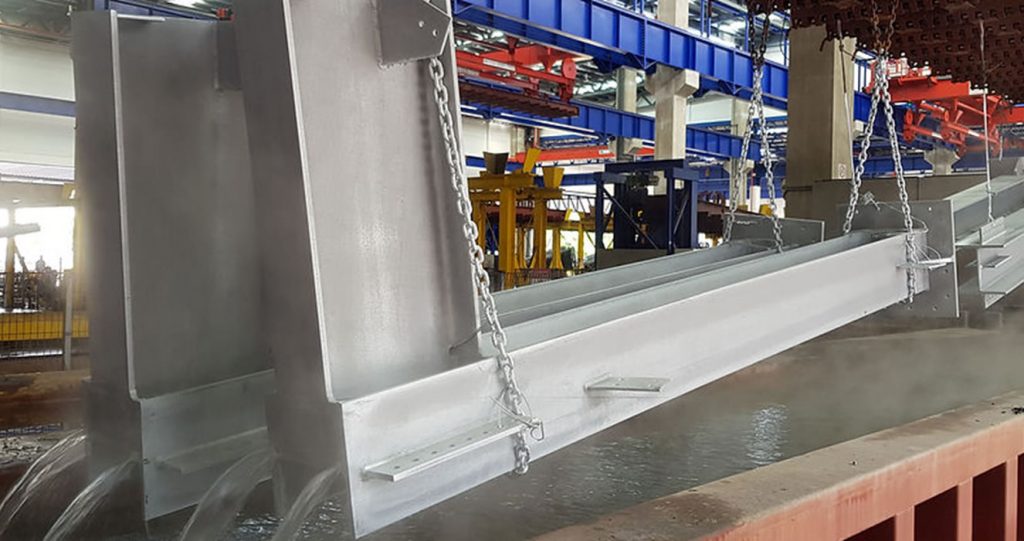
Galvanization is a process that coats metal with zinc-iron alloy layers. The zinc protects the metal from corrosion and gives it a silver color. Hot-Dip Galvanizing is often used on steel to protect it from rusting. In this blog post, we will explain the galvanizing process in detail!
Quick Overview
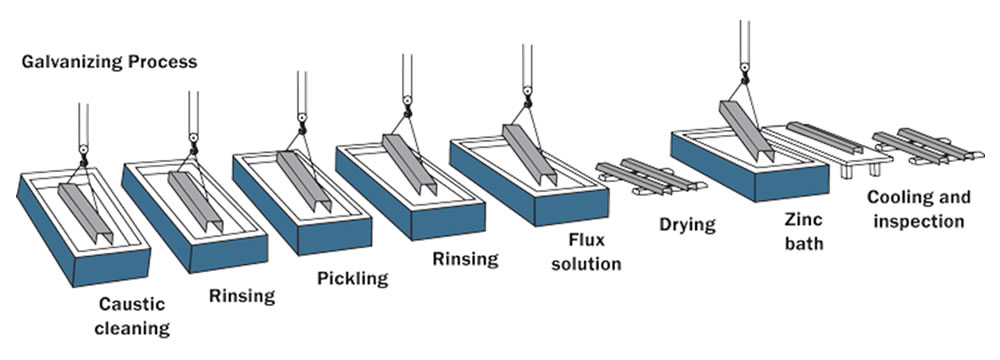
The entire galvanizing process consists of different steps as below:
- Pre-Consideration & Loading: This step includes draining holes and loading the item properly before sending it to pre-treatment.
- Pre-treatment: It consists of degreasing, and acid pickling, followed by pre-fluxing.
- Zinc coating: The steel is dipped in a molten zinc bath and cooled.
- Finishing: After the galvanizing process, some final finishing touches are applied, such as the removal of zinc spikes.
Pre-Galvanizing Consideration
There are some considerations before sending your materials for galvanizing. This will help ensure that the galvanizing coating is of the best quality.
Draining / Vent Holes
When fabricating steel for galvanizing, it is essential to consider the placement of drainage and vent holes. Ideally, each item should have two holes at each end, placed in the fabrication plane.
These holes should be diagonally opposite each other, and external holes should be placed as close to the connection as possible. This will help ensure that the galvanized coating is evenly applied and that any excess zinc can drain properly.
Cropped Corners / Notches
One of the considerations when pre-galvanizing is ensuring that there are no cropped corners or notches. This is because these can act as sites for corrosion to start.
The notches also need to be taken into account to ensure that the coating is evenly applied and there are no areas where the zinc is thinner and more vulnerable to corrosion.
Lifting & Hooking Points
The placement of lifting and hooking points must be positioned in such a way that the materials can be easily loaded onto the jigs while still allowing for proper draining.
If the fluid cannot flow in and out quickly and evenly, it can result in an uneven or blotchy finish. By taking the time to position these points properly, manufacturers can help ensure a high-quality galvanized product.
Material Condition – Rusty, Oily, painted & Lacquered
The pre-existing conditions such as rust, oil, paint, and lacquer can pose a problem for the galvanization process. If these coatings are not removed before galvanization, they can prevent the new coating from forming properly.
This can lead to uncoated areas, surface roughness, and peeling galvanized coatings. As a result, it’s important to make sure that materials are clean and free of any coatings before they undergo galvanization.
Special pre-treatment methods such as sandblasting can be used to remove these coatings and ensure that the galvanization process runs smoothly.
The 8 Steps of the Hot-Dip Galvanizing Process
Step 1 – Degreasing
The galvanizing process begins with removing oil and grease from the surface of the steel. This is done using a hot alkaline cleaning solution.
The solution breaks down the oil and grease, allowing it to be rinsed away. This step is important because it ensures that the steel is clean and ready for the next step in the process.
Step 2 – Rising
The second step of the galvanizing process is rinsing. This is done to remove any alkaline that may be present on the surface of the metal. If alkaline were to come into contact with the pickling solution, it would prevent the acid from doing its job, wasting both time and resources.
To rinse the metal, it is passed through a bath of clean water. The water must be high enough to remove all traces of alkaline but not so hot that it damages the metal.
Step 3 – Scale Removal or Pickling
The third step in the galvanizing process is known as scale removal or pickling. The steel is cleaned by being put in an acid bath. This removes the surface rust and mill scale.
The steel is now ready for the next step: putting a layer of zinc on it. The pickling stage is vital to the overall quality of the final product, as it ensures that the zinc coating will be evenly applied and will provide optimum protection against corrosion.
Step 4 – Rising After Pickling
After the pickling process is completed, the next step is to rinse off the steel in order to remove any residual acid or iron salt. The rinse water must be clean and free of impurities, as these can quickly cause corrosion. Once the rinse is complete, the steel is ready for further processing.
Step 5 – Pre-Fluxing
The surface of the steel must be clean before it is dipped in molten zinc. The steel is cleaned by dipping it in a hot flux solution. This usually contains zinc ammonium chloride. This helps stop the surface from becoming oxidized and prepares it for the next step in the process.
Step 6 – Zinc Bath
The next step in the galvanizing process is the zinc bath. Here, the steel product is put into a vat of molten zinc. The zinc reacts with the steel to form a protective layer.
The time it spends in the vat depends on how much zinc is used and the weight of the steel product. Once the desired zinc coating thickness is achieved, the fabrication is withdrawn from the zinc bath and cooled.
Step 7 – Quenching
The steel is slowly taken out of the molten zinc bath so that an oxide skin doesn’t form. Alloy layers and pure zinc layers are also created when the steel is chilled in water.
This zinc coating is attached to the steel to cover the entire article. Quenching provides protection for the steel and gives the galvanized item a distinct brightness and luster.
Step 8 – Finishing
The final step in the galvanizing process is known as de-racking, where the hot-dip galvanized steel is transferred for a final inspection. This is when bare spots are touched and sharp edges removed.
This ensures that all materials are ready for their final destination, whether installation or further processing. Once all of the materials have been de-racked, the galvanizing process is complete.
Conclusion
The galvanizing process is a critical step in the fabrication of steel products. By understanding the steps involved, you can ensure that your materials are properly protected against corrosion. We are the leading provider of galvanizing services in Malaysia, so contact us today to learn more about how we can help you.

